Water efficiency in landscapes and building design


Irrigation
Smart Irrigation technology utilizes rain sensors to conserve water by only irrigating when needed. 45 of our 57 irrigation systems employ this technology, and the 12 that are too small to utilize it use solar-powered timers.

Rain water capture and reuse
Rainwater recovery systems is utilized to power two irrigation systems. Rainwater from the roof of Glick Eye Institute and SELB are collected and held in cisterns. This recovered water is then used to supply drip irrigation to the surrounding landscapes.

Low-flow fixtures
IU Indianapolis employs low-flow faucets, toilets, and showers across campus to make water use as efficient as possible. Thanks to a winning Greening IU Indianapolis Grant, low-flow toilet handles were installed in some of IU Indianapolis's oldest buildings, saving campus an estimated 1 million gallons of water annually.

Water runoff
Structural stormwater controls have been implemented to reduce the pollutant load of campus stormwater runoff. In addition to structual controls, IU Indianapolis also has rain gardens which retain and filter runoff, reducing up to 30% of the pollutants.
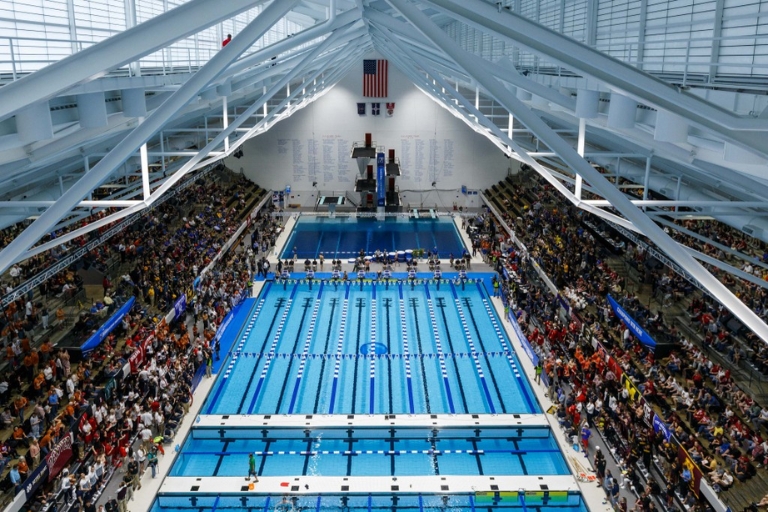
Water conservation at the Natatorium
The Indiana University Natatorium in Indianapolis has implemented several measures to enhance water conservation and efficiency.During its renovation, the facility upgraded its plumbing systems to improve water quality and efficiency.

Take action
Conserve water
There are many simple ways to conserve water on a daily basis including turning the water off while brushing teeth and turning the shower on only during the actual shower period.
Wash water with full loads
Wash laundry with full load to conserve water. Additinally, cool water cleans just as effectively as warm water.
Flush appropriately
Avoid flushing items that harm sewage systems like 'flushable' wipes, feminine hygiene items, hypodermic needles, and prescription medication.

